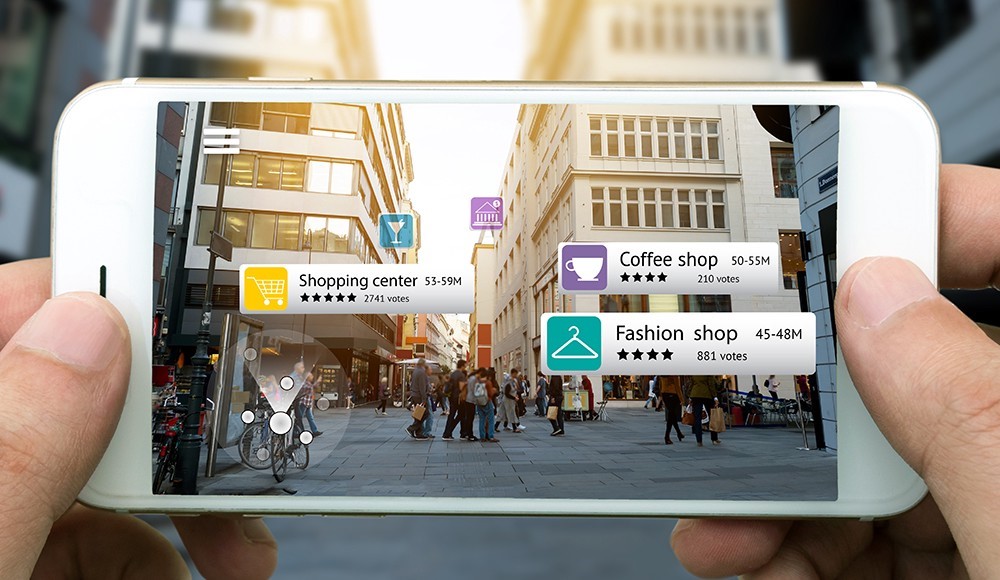
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (or AR) is a technology that superimposes a computer data, graphics, audio and other sensory enhancements on a user’s view of the environment that is displayed in real time, thus providing a composite view.
AR has been called the next big paradigm shift in computing, tantamount to the kind of transformational changes that the internet and the smartphone made in the field. Global technology leaders, including Google, Microsoft, Facebook, Snapchat, and Apple, have all staked significant claims in the AR “digital” land rush.
AR is most valuable in the public sector when it is “lighting up” real data, whether those data are:
- accessible through the open government data initiatives (that are rapidly taking hold at every level),
- being generated by the growing sensor-based networks and smart infrastructure (that are spreading across the environment), or
- capturing the massive amount of unstructured data (being created every day by mobile users, the growing formal and informal networks resulting from the sharing economy, and other structured and unstructured data sources).
With the combination of smart infrastructure, big data and open data, public sector entities at all levels are able to start stitching together the fabric for smart cities, smart solutions, and connected and cross-platform solutions to actually deliver integrated services and experiences to citizens and allow workers to operate in that kind of environment. AR serves as the visual portal to data across the public and private sectors, adding huge value to prospect of data as true public asset and resource.
Over the past few years, the core AR software and, most important, the devices that will deliver the augmented reality experiences, have finally begun to mature. They include:
- Handhelds and mobile devices, primarily smartphones and tablets, and built-for-purpose mobile workforce devices
- Head-up displays (HUDs) for windshields, screens, visors
- Head mounted displays (HMDs)
- Glasses, goggles, visors and helmets
- Contact lenses, virtual retina displays
- Spatial displays
Check out these potential uses already being planned or in the proof of concept stage for a cursory overview of the possibilities:
6 ways augmented reality can help governments see more clearly (Feb 13, 2017)
